Are you concerned about the health of your gums and teeth? Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common but preventable oral health issue that affects many individuals.
In this article, we will explore what periodontal disease is, what causes it, and the signs and symptoms to look out for. We will also discuss the best ways to prevent this condition, such as maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding smoking, eating a balanced diet, and visiting your dentist regularly.
Stay tuned to learn more about keeping your gums and teeth healthy!
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a serious condition that affects the health of the gums and the surrounding structures that support the teeth. It is a chronic inflammatory disease caused by bacteria that accumulate on the teeth and gums.
If left untreated, periodontal disease can progress through various stages, starting with gingivitis, which is the mildest form characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. As the disease advances, it can lead to periodontitis, where the gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected.
Risk factors for developing periodontal disease include poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, certain medications, and chronic illnesses like diabetes. Complications of untreated gum disease include tooth loss, bone damage, and an increased risk of systemic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
What Causes Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is primarily caused by the build-up of dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. When plaque is not removed through proper oral hygiene practices, it can harden into tartar, leading to gum inflammation and infection.
This bacterial invasion triggers the body’s immune response, causing the gums to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets where more bacteria thrive. As the infection progresses, it can damage the bone supporting the teeth, ultimately leading to tooth loss. The cycle of plaque accumulation, bacterial growth, and inflammation underscores the critical need for regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings to prevent and treat periodontal disease effectively.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene, characterized by inadequate brushing and flossing practices, is a leading cause of periodontal disease. When plaque is not effectively removed from the teeth and gum line, it can lead to the accumulation of harmful bacteria that trigger gum inflammation and potential infection.
This emphasizes the crucial role of maintaining proper oral hygiene habits to prevent the onset and progression of periodontal disease. Brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and using proper flossing techniques are essential steps in removing plaque and food particles that can contribute to gum disease. Scheduling regular dental cleanings and check-ups can help detect any early signs of periodontal issues, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further complications.
Good oral hygiene not only protects your gums and teeth but also plays a significant role in maintaining overall dental health.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking and tobacco use are significant risk factors for the development and progression of periodontal disease. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco products can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections in the gums and supporting tissues.
As periodontal disease progresses, it can lead to serious complications such as gum recession, bone loss, and ultimately tooth loss. The negative impact of tobacco on gum health is also seen in delayed healing after oral surgeries and increased risk of developing oral cancer. Individuals who smoke are more likely to have deeper gum pockets, which provide a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
Quitting smoking is crucial for improving oral health and reducing the risk of gum disease. Making lifestyle changes, seeking support from healthcare professionals, and utilizing nicotine replacement therapies can aid in successful smoking cessation.
Genetics
Genetic factors can play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to periodontal disease. Certain genetic markers can predispose some individuals to develop more severe forms of gum disease, even with diligent oral hygiene practices.
Research suggests that individuals with specific genetic variations may produce higher levels of inflammatory proteins in response to bacterial plaque build-up, leading to increased risk of gum inflammation and tissue damage.
Understanding these genetic predispositions can empower individuals to take proactive measures in oral care, such as regular dental check-ups, professional cleanings, and personalized treatment plans.
By addressing genetic risk factors early on, individuals can potentially mitigate the impact of genetics on their gum health and maintain optimal oral hygiene in the long run.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders, can increase the risk of periodontal disease due to their impact on the body’s inflammatory response and immune system. Conditions that compromise overall health can also affect gum health and contribute to gum inflammation.
For instance, individuals with conditions like heart disease or respiratory issues may experience reduced blood flow or compromised oxygen levels, affecting the ability of gum tissues to heal and fight off infections. Systemic illnesses like osteoporosis can lead to bone density loss, impacting the support structure for teeth and making them more susceptible to periodontal problems. Therefore, it is crucial for those with underlying health concerns to prioritize managing their conditions through regular medical check-ups, a balanced diet, and proper medication to reduce the risk of developing or worsening gum disease.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease?
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of periodontal disease is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Common indicators of gum disease include gum inflammation, persistent bad breath, gum bleeding, and changes in the appearance or alignment of the teeth.
Other signs that may point to the presence of periodontal disease include receding gums, loose teeth, pain while chewing, and pockets forming between the teeth and gums.
Individuals with advanced periodontitis may experience pus between the teeth and gums, sensitivity to hot or cold, and a change in the way their teeth fit together when biting.
It’s vital to understand that untreated gum disease can lead to serious consequences such as tooth loss, bone damage, and even systemic health issues if bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream.
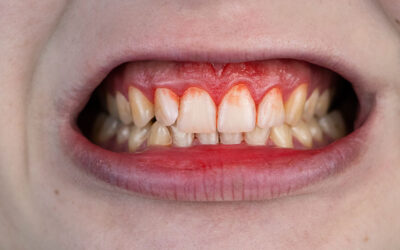
Swollen or Bleeding Gums
Swollen or bleeding gums are common early signs of periodontal disease, indicating inflammation and potential infection in the gum tissue. When gums appear red, swollen, or bleed easily during brushing or flossing, it may be a signal of underlying gum health issues.
Such symptoms often arise due to the presence of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that accumulates on teeth. If not removed through proper oral hygiene practices like brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to gum irritation and inflammation. The bacteria in plaque release toxins that harm the gum tissue, causing it to become swollen and prone to bleeding. Addressing these symptoms promptly is crucial to prevent further progression of periodontal disease and maintain overall oral health.
Bad Breath
Persistent bad breath, also known as halitosis, can be a sign of underlying periodontal disease. The presence of bacteria in the mouth, often resulting from poor dental hygiene practices, can lead to foul-smelling breath that persists despite oral care efforts.
The correlation between bad breath and periodontal disease is closely linked as the buildup of bacteria in the mouth contributes significantly to halitosis. These bacteria release sulfur compounds, causing the unpleasant odor associated with bad breath. To combat this, individuals can enhance their dental hygiene by brushing teeth twice a day, flossing regularly, and using mouthwash. Maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated can help in reducing oral malodor. Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in identifying and addressing any underlying issues that may be causing persistent bad breath.
Loose Teeth
Loose or shifting teeth can be a late-stage symptom of advanced periodontal disease, indicating significant damage to the supporting structures of the teeth. When gum health deteriorates due to untreated gum disease, teeth may become unstable and mobile.
This tooth mobility is a direct result of the infection and inflammation that weaken the ligaments and bone supporting the teeth. It’s crucial to address loose teeth promptly, as they can lead to further complications such as tooth loss if left untreated.
Seeking professional dental care is imperative in such cases, as dentists can assess the extent of the damage and recommend appropriate treatment. Treatment options for stabilizing loose teeth may include deep cleaning procedures like scaling and root planing, antibiotics to address the infection, and in severe cases, surgery to repair damaged tissues and restore stability to the teeth.
Receding Gums
Gum recession, characterized by the exposure of tooth roots and a loss of gum tissue height, is a common indicator of periodontal disease progression. Receding gums can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, aesthetic concerns, and susceptibility to further oral health issues.
This condition often develops due to factors such as poor oral hygiene, aggressive brushing techniques, genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and smoking. As gum tissue pulls away from the teeth, it creates pockets that harbor harmful bacteria, leading to inflammation and infection. If left untreated, periodontal disease can advance, causing irreversible damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
Treatment options for gum recession may include scaling and root planing, gum grafting, or in severe cases, surgical interventions. To prevent gum recession, it is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene practices, attend regular dental check-ups, and avoid habits that contribute to gum tissue erosion.
Changes in Bite or Tooth Alignment
Changes in bite or tooth alignment, such as gaps between teeth, shifting of dental arches, or alterations in the way the upper and lower teeth fit together, can be indicative of underlying gum health issues. Periodontal disease can affect the stability and positioning of teeth over time.
This impact on tooth alignment is a result of the inflammation and infection that characterize periodontal disease. As the gums recede and bone supporting the teeth is compromised, the structural integrity of the teeth can be compromised, leading to misalignment.
Addressing these bite changes is crucial for maintaining overall oral health, as misaligned teeth can cause uneven wear, jaw pain, and difficulties in chewing. Periodontal treatments, such as deep cleaning procedures and gum grafts, play a significant role in restoring tooth alignment by addressing the underlying gum health issues.
How Can Periodontal Disease Be Prevented?
Preventing periodontal disease involves adopting effective oral hygiene practices, making healthy lifestyle choices, and prioritizing regular dental check-ups. By implementing preventive measures and seeking timely dental care, individuals can reduce their risk of developing gum disease and maintain optimal oral health.
- Good oral hygiene is fundamental in preventing periodontal disease, including brushing and flossing daily to remove plaque buildup.
- Quitting smoking is crucial as it significantly reduces the risk of gum disease.
- Consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients also plays a key role in promoting gum health.
Regular visits to the dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups are essential to catch any signs of gum disease early. Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, can also help prevent complications related to oral health.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene
One of the most effective ways to prevent periodontal disease is to practice good oral hygiene consistently. This includes brushing teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and scheduling regular dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Proper brushing technique involves using a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle circular motions to clean each tooth thoroughly. It’s important to also brush the tongue to remove bacteria and freshen breath.
When flossing, ensure you gently glide the floss between teeth and along the gumline to remove plaque and food particles.
Mouthwash can help reduce plaque and bacteria in hard-to-reach areas.
Professional dental cleanings play a vital role in deep cleaning the teeth and gums, targeting areas that are difficult to clean effectively at home.
Quit Smoking and Avoid Tobacco Use
Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco use are essential steps in preventing periodontal disease. By eliminating the harmful effects of tobacco on oral health, individuals can reduce their risk of gum inflammation, infections, and other complications associated with smoking.
Smoking not only hinders blood flow to the gums, making it harder for them to heal, but it also weakens the immune system, making it less effective in fighting off bacteria that cause gum disease.
To effectively quit smoking, individuals can seek support from healthcare professionals, utilize nicotine replacement therapy, join support groups, or try behavioral therapy. Once an individual stops smoking, their gum health can significantly improve, leading to decreased risk of gum disease, stronger teeth, fresher breath, and a brighter smile.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and nutrients is crucial for promoting gum health and preventing periodontal disease. Consuming foods that are low in sugar and high in fiber can help reduce plaque buildup and support overall oral health.
Incorporating nutrient-dense foods like leafy greens, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can contribute to strong teeth and gums. Vitamins such as Vitamin C and Vitamin D play vital roles in gum health, while minerals like calcium and phosphorus aid in maintaining the strength of teeth. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish can help reduce inflammation in the gums.
By focusing on a well-rounded diet and limiting sugary snacks and beverages, individuals can significantly improve their oral hygiene and prevent gum disease.
Visit the Dentist Regularly
Regular dental check-ups are essential for preventing periodontal disease and maintaining optimal oral health. Dental professionals can detect early signs of gum disease, provide professional cleanings, and offer guidance on effective oral hygiene practices to prevent dental issues.
Routine dental visits play a vital role in catching gum problems in their early stages, preventing them from progressing into more serious issues. Professional cleanings help remove plaque buildup, reducing the risk of gum inflammation and infections. Making the most out of dental appointments involves openly discussing any concerns with your dentist, following their advice for at-home care, and scheduling regular check-ups to ensure any potential problems are addressed promptly.
Manage Health Conditions
Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease, is crucial for maintaining periodontal health and preventing gum disease. Conditions that impact the immune system or inflammatory response can increase the risk of gum infections and inflammation.
The relationship between systemic health conditions and gum health is significant as diseases like diabetes can affect the body’s ability to fight off infections, including those in the gums. Cardiovascular issues may also contribute to gum disease due to compromised blood flow affecting the gums.
To manage these chronic illnesses effectively in relation to oral health, individuals should prioritize regular dental check-ups, maintain good oral hygiene practices, and communicate with both their dentist and healthcare team. Taking a holistic approach to health management not only improves overall well-being but also plays a crucial role in preventing the onset and progression of gum disease.